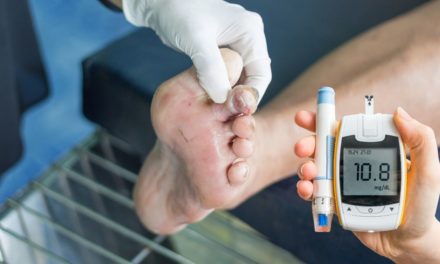
Diabetic foot care is crucial for individuals with diabetes to maintain optimal wellness. Diabetes can also lead to nerve damage and poor blood circulation in the body which increasing the risk of foot problems. Here are the healthy steps involved:
1. Daily Inspection: Check your feet daily for any cuts, blisters, redness, or swelling. Diabetes can lead to reduced sensation, so you might not feel these issues without actively looking for them.
2. Keep Feet Clean: Wash your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap. Dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes, to prevent fungal infections.
3. Moisturize: Apply a gentle moisturizer to prevent cracking, but avoid applying it between the toes as excess moisture can lead to infections.
4. Trim Nails Carefully: Trim your nails straight across and file the edges to avoid ingrown nails. If you have difficulty seeing or reaching your feet, consider having a podiatrist trim your nails.
5. Proper Footwear: Wear comfortable, well-fitting shoes to avoid friction and pressure points. Choose shoes with ample toe room and cushioning. Avoid tight, pointed, or high-heeled shoes.
6. Diabetic Socks: Wear seamless, moisture-wicking diabetic socks that reduce the risk of blisters and provide cushioning.
7. Avoid Bare Feet: Always wear shoes or slippers to protect your feet, even indoors. This prevents accidental injuries.
8. Check Shoes: Inspect your shoes before putting them on to make sure there are no foreign objects inside that could cause injury.
9. Manage Blood Sugar: Keep your blood sugar levels under control through proper medication, diet, and exercise. Stable blood sugar levels promote better foot health.
10. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity to improve blood circulation for maintaining a healthy weight. Consult your doctor for exercise recommendations tailored to your condition.
11. Avoid Smoking: Smoking can further reduce blood circulation, which is already compromised in individuals with diabetes.
12. Foot Exams: Schedule regular foot exams with a healthcare professional or podiatrist. They can identify potential issues early and offer guidance on foot care.
13. Prompt Treatment: If you notice any cuts, sores, or infections, seek prompt medical attention. Delaying the treatment can also lead to serious complications.
14. Manage Peripheral Neuropathy: Diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage) is common. Managing it with your healthcare provider can prevent loss of sensation and foot injuries.
15. Elevate Feet: Elevate your feet when sitting to improve blood circulation and reduce swelling.
Remember, diabetic foot care is a lifelong commitment. By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of foot-related complications and ensure your overall well-being. If you have specific concerns or conditions, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance.