Introduction
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are a group of conditions that affect the muscles, bones, tendons, ligaments, and other connective tissues, causing pain, discomfort, and restricted mobility. These disorders have become increasingly prevalent in today’s sedentary lifestyle and can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. In this article, we will explore the common types of MSDs, their causes, risk factors, and most importantly, how to prevent and manage these conditions to lead a healthy and pain-free life.
Types of Musculoskeletal Disorders
There are several types of MSDs, each affecting different parts of the musculoskeletal system. The most common ones include:
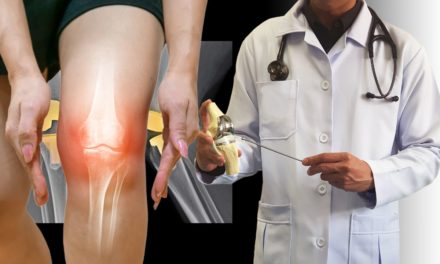
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain and stiffness in the affected joints.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder that causes chronic inflammation of the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and eventual joint deformities.
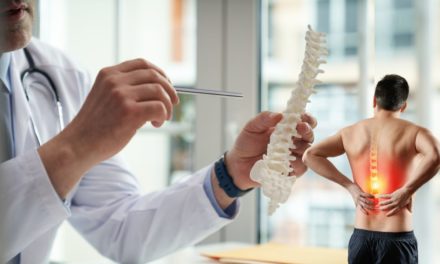
- Back Pain: A widespread issue affecting the spine, causing discomfort and limited mobility.
- Neck Pain: Often caused by poor posture, muscle strain, or injury, resulting in stiffness and discomfort in the neck region.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A condition caused by compression of the median nerve in the wrist, leading to numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons, usually caused by repetitive movements or overuse.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of MSDs is essential in preventing their development. Some common causes and risk factors include:
- Poor Posture: Prolonged sitting or standing in improper positions can put strain on the musculoskeletal system.
- Repetitive Motions: Engaging in repetitive movements, such as typing or lifting, can lead to overuse injuries.
- Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle weakens muscles and bones, making them more susceptible to injuries.
- Aging: As we age, the wear and tear on our joints and tissues increase, making older adults more prone to MSDs.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional stress on the joints, increasing the risk of developing MSDs.
- Trauma and Injuries: Accidents or sports-related injuries can damage the musculoskeletal system.
Prevention and Management
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga can strengthen muscles and joints, reducing the risk of MSDs.
- Proper Ergonomics: Maintaining good posture and using ergonomically designed furniture and tools can prevent strains caused by repetitive tasks.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the stress on joints and minimize the risk of developing MSDs.
- Avoiding Prolonged Inactivity: Taking breaks during extended periods of sitting or standing can help prevent stiffness and discomfort.
- Injury Management: Promptly treating and rehabilitating any injuries can prevent long-term complications and chronic MSDs.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in nutrients, particularly calcium and vitamin D, supports bone health and prevents osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Musculoskeletal disorders can significantly impact one’s quality of life, causing pain and hindering daily activities. By understanding the types, causes, and risk factors associated with MSDs, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent their development. Regular exercise, maintaining proper ergonomics, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are key steps in promoting a pain-free musculoskeletal system. Remember, prevention is the best cure, so take care of your body today to enjoy a more active and fulfilling life tomorrow.